03/02/2010

BELO HORIZONTE - MG ESCOLA DE EDUCACAO BASICA E PROFISSIONAL DA UFMG - CENTRO PEDAGOGICO
Luciana de Oliveira Silva
| Modalidade / Nível de Ensino | Componente Curricular | Tema |
|---|---|---|
| Ensino Médio | Língua Estrangeira | Produção oral |
| Ensino Médio | Língua Estrangeira | Compreensão leitora |
| Ensino Médio | Língua Estrangeira | Produção escrita |
O que o aluno poderá aprender com esta aula
O aluno aprenderá o conceito de multiple intelligences e a importância dessa teoria no dia-a-dia escolar. Usará o skimming e scannning na leitura de textos sobre o que é inteligência e inteligências múltiplas.
Duração das atividades
Conhecimentos prévios trabalhados pelo professor com o aluno
Relative clauses com: who, that, which and whose.
Estratégias e recursos da aula
Aula 1
Instigue os alunos perguntando:
What is intelligence for you?
Incentive os aprendizes a responderem da forma que souberem. Anote as respostas no quadro, pois, assim todos saberão o conceito de inteligência estabelecido pela turma.
Após formarem um conceito de inteligência, distribua o texto a seguir para cada um dos alunos.
“Intelligence is a term that is difficult to define, and it can mean many different things to different people. In fact, it has divided the scientific community for decades and controversies still rage over its exact definition and form of measurement.
In the popular sense, intelligence is often defined as the general mental ability to learn and apply knowledge to manipulate your environment, as well as the ability to reason and have abstract thought. Other definitions of intelligence include adaptability to a new environment or to changes in the current environment, the ability to evaluate and judge, the ability to comprehend complex ideas, the capacity for original and productive thought, the ability to learn quickly and learn from experience and even the ability to comprehend relationships.
A superior ability to interact with the environment and overcome its challenges is often seen as a sign of intelligence. In this case, the environment does not just refer to the physical landscape (eg. mountains, forests) or the surroundings (eg. school, home, workplace) but also to a person’s social contacts, such as colleagues, friends and family – or even complete strangers.
Researchers asked about the aspects of intelligence felt that factors like problem-solving ability, mental speed, general knowledge, creativity, abstract thinking and memory all played important roles in the measure and standard of intelligence. Most agree that intelligence is an umbrella term which covers a variety of related mental abilities.”
Texto adaptado de http://www.aboutintelligence.co.uk/what-intelligence.html (acesso em 07 de Dezembro de 2009)
Sugestão: Acesse: http://sites.google.com/site/centropedagogicoufmg/lingua-estrangeira-1/luana-vieira/intelligence (acesso em 07 de Dezembro de 2009) para ter cópias do texto sugerido acima. Neste arquivo, você encontrará um glossário que ajudará os alunos na compreensão do texto.
Observação:
Ensine aos alunos os processos de leitura: Skimming e Scanning. Mostre a eles que conhecendo essas duas estratégias, ficará mais fácil ler qualquer tipo de texto.
Skimming: é passar os olhos rapidamente sobre o texto para se ter uma idéia geral do é tratado no texto. As primeiras e últimas frases de cada parágrafo são importantes, pois, normalmente sintetizam o que trata o texto.
Scanning: esse processo vem da idéia de scanear. Passar os olhos de uma maneira que você consiga reter informações específicas.
Depois, passe as seguintes perguntas aos alunos:
1- What is the main topic focused on the text? Answer: The text discussed what intelligence is.
2- According to the text, what is intelligence in the popular sense? Answer: intelligence is often defined as the general mental ability to learn and apply knowledge to manipulate your environment, as well as the ability to reason and have abstract thought.
3- Cite two other characteristics that define intelligence: Answer: A superior ability to interact with the environment and overcome its challenges is often seen as a sign of intelligence. In this case, the env ironment does not ju st refer to the physical landscape (eg. mountains, forests) or the surroundings (eg. school, home, workplace) but also to a person’s social contacts, such as colleagues, friends and family – or even complete strangers; adaptability to a new environment or to changes in the current environment.
4- According to the researchers, what are the important roles to measure the intelligence?
Answer: Researchers asked about the aspects of intelligence felt t hat factors like problem -solving ability, mental speed, general knowledge, creativity, abstract thinking and memory all played important roles in the measure and standard of intelligence.
5)- The text compare the intelligence with a common object. Which object is this? Why? Answer : Most agree that intelligence is an umbrella term which covers a variety of related mental abilities.”
Corrija oralmente as respostas dos alunos. É ideal que você tenha o texto impresso de uma maneira que todos possam vê-lo (ppt, retroprojetor, cartolina, etc). Desse modo, a correção ocorrerá de forma rápida e eficiente.
Aula 2
Nesta aula você irá introduzir o conceito de Multiple Intelligences. É interessante que os alunos conheçam tal conceito, pois muitos não respeitam (ou não entendem) as diferenças existentes dentro de uma sala de aula. Alguns se envergonham, simplesmente por não terem a mesma facilidade que um colega tem com cáculos. Por sua vez, o aluno que possui facilidade com números pode não entender a razão de ter dificuldades para escrever, por exemplo.
Mostre aos aprendizes a figura a seguir e as seguintes classificações:
- Linguistic
- Intrapersonal
- Interpersonal
- Musical
- Naturalist
- Kinesthetic
- Spatial
- Logic/ Math
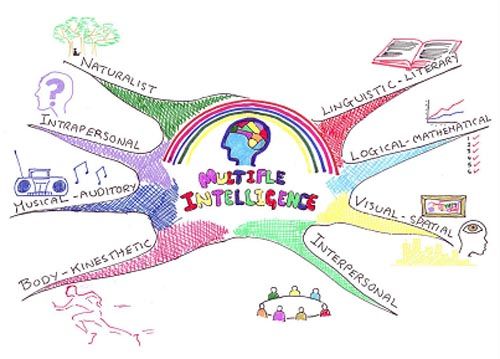
Figura 1: Multiple Intelligence.
Fonte: http://www.brainleadersandlearners.com/wp-content/uploads/2008/10/multiple-intelligences.jpg (acesso em 07 de Dezembro de 2009)
Pergunte:
What do they mean?
Incentive-os a relacionarem os termos dados com o vocabulário já conhecido pelos mesmos.
Se voce tiver acesso ao laboratório de informática, peça aos alunos que façam o seguinte teste: http://literacyworks.org/mi/assessment/findyourstrengths.html (acesso em 07 de Dezembro de 2009). Este teste fornece 56 questões que avaliarão qual é o tipo de inteligência inerente a cada aluno. Explique que eles acharão 8 resultados diferentes (termos mencionados acima), sendo que os três mais evidentes, de acordo com cada pessoa, serão apresentados primeiro.
Caso não possua acesso ao laboratório de informática, acesse: http://sites.google.com/site/centropedagogicoufmg/lingua-estrangeira-1/luana-vieira/intelligence (acesso em 07 de Dezembro de 2009) para imprimir o teste em questão. Sugerimos que divida a sala em duplas para a resolução do mesmo. Após os alunos responderem o teste, siga as instruções dadas para conseguir o resultado. Verifique em quais perguntas os alunos deram 5, 4, 3 etc. Oriente-os posteriormente, a identificar qual inteligência está relacionada com cada questão.
ATENÇÃO!
Você deverá reconhecer, caso utilize o teste de modo impresso, qual das inteligências cada questão está relacionada. Veja o exemplo:
1. I pride myself on having a large vocabulary. – Linguistic Intelligence.
Peça a voluntários que apresentem seus resultados à classe. Eles deverão le r o resultado apresentado no quiz e dizer se concordam ou não com o mesmo.
Aula 3
Distribua aos alunos um texto que aborda o conceito de Multiple Intelligences.
The theory of multiple intelligences was deve loped in 1983 by Dr. Howard Gardner, professor of education at Harvard University. It suggests that the traditional notion of intelligence, based on I.Q. testing, is far too limited. Instead, Dr. Gardner proposes eight different intelligences to account for a broader range of human potential in children and adults. These intelligences are:
Linguistic intelligence ("word smart"):
Logical-mathematical intelligence ("number/reasoning smart")
Spatial intelligence ("picture smart")
Bodily-Kinesthetic intelligence ("body smart")
Musical intelligence ("music smart")
Interpersonal intelligence ("people smart")
Intrapersonal intelligence ("self smart")
Naturalist intelligence ("nature smart")
Dr. Gardner says that our schools and culture focus most of their attention on linguistic and logical-mathematical intelligence. We esteem the highly articulate or logical people of our culture. However, Dr. Gardner says that we should also place equal attention on individuals who show gifts in the other in telligences: the artists, architects, musician s, natur alists, designers, dancers, therapists, entrepreneurs, and others who enrich the world in which we live. Unfortunately, many children who have these gifts don’t receive much reinforcement for them in school. Many of these kids, in fact, end up being labeled "learning disabled," "ADD (attention deficit disorder," or simply underachievers, when their unique ways of thinking and learning aren’t addressed by a heavily linguistic or logical-mathematical classroom. The theory of multiple intelligences proposes a major transformation in the way our schools are run. It suggests that teachers be trained to present their lessons in a wide variety of ways using music, cooperative learning, art activities, role pl ay, multimedia, field trips, inner reflection, and much more (see Multiple Intelligences in the Classroom). The good news is that the theory of multiple intelligences has grabbed the attention of many educators around the country, and hundreds of schools are currently using its philosophy to redesign the way it educates children. The bad news is that there are thousands of schools still out there that teach in the same old dull way, through dry lectures, and boring worksheets and textbooks. The challenge is to get this information out to many more teachers, school administrators, and others who work with children, so that each child has the opportunity to learn in ways harmonious with their unique minds (see In Their Own Way).
Texto adaptado de http://www.thomasarmstrong.com/multiple_intelligences.htm (acesso em 07 de Dezembro de 2009)
Sugestão: Acesse: http://sites.google.com/site/centropedagogicoufmg/lingua-estrangeira-1/luana-vieira/intelligence (acesso em 07 de Dezembro de 2009) para ter cópias do texto sugerido acima. Neste arquivo, você encontrará um glossário que ajudará os alunos na compreensão do texto.
Novamente, use os recursos de scan e skim para facilitar a leitura do texto com os alunos.
Observação: Esclareça dúvidas em relação ao vocabulário contido no texto.
Logo depois, pergunte aos alunos:
1)- Who and when the theory was developed?
Answer: Professor Howard Gardner in 1983.
2)- What are the eight intelligences suggested in the theory?
Answer: Linguistic, Logical/math, Spatial, Kinesthetic, Musical, Interpersonal, Intr apersonal and Naturalist
3)- According to the quiz solved in class 2, give two characteristics of each of the intelligences.
4)- What are the intelligences that receive more focus on the schools nowadays?
Answer: Linguistic and Logical / Math intelligences.
5)- What happens to people who do not have these intelligences?
Answer: They are finally labeled as not able to learn.
Corrija os exercícios propostos. Sugerimos que você tenha o texto em mãos e de uma forma que os alunos possam visualizá-lo.
Aula 4
Nesta aula os alunos irão descrever, usando relative clauses (who, which, that e whose), cada uma das inteligências propostas na teoria estudada.
Divida a sala em pequenos grupos. Eles deverão entrevistar uns aos outros dentro de sala de modo que obtenham o maior número de informações sobre a determinada inteligência. Perguntas como: Você tem mais facilidade com números ou palavras? Você prefere ler ou praticar esportes? etc. deverão ser respondidas.
Por fim, os alunos deverão reportar ao restante da sala, usando cartazes, figuras, palavras-chave, etc., as características de três pessoas que eles entrevistaram posteriormente.
Ex: Eliane is a student who is good at English and Spanish. Her main intelligence is Linguistic. A person who has the Linguistic intelligence….
Observação: Os alunos devem fornecer o maior número de informações possível.
Recursos Complementares
RECURSO –
Dictionary.com
http://portaldoprofessor.mec.gov.br/link.html?pagina=1&tamanhoPagina=25&categoria=3&outrosPaises=false
(acesso em 07 de Dezembro de 2009)
Avaliação
Divida a sala em grupos de oito pessoas. Cada pessoa ficará responsável para a elaboração de 5 perguntas referentes à um tipo de inteligência.Todos os grupos deverão criar um quiz, semelhante ao usado na aula 2.
Cada grupo escolherá um professor da escola. Pergunte aos seus colegas de trabalho, se eles se importam em participar da sua aula. Por exemplo: o grupo 1, já com seu quiz pronto escolhe o professor de Biologia da escola. Eles deverão fazer o quiz com este professor e verificar se a inteligência predominante dele corresponde ao que ele ensina.
Observação: Deixe claro aos alunos que a teoria de Inteligências Múltiplas é uma teoria. O professor de Biologia pode ter, de acordo com o teste, uma inteligência lógica/matemática aguçada.
Depois do teste feito, incentive-os a fabricarem cartazes com características da pessoa entrevistada. Para isso, saliente que, além das respostas para o teste, os aprendizes deverão tomar nota de todas as informações dadas pelo entrevistado.
Sem estrelas 0 classificações
- Cinco estrelas 0/0 - 0%
- Quatro estrelas 0/0 - 0%
- Três estrelas 0/0 - 0%
- Duas estrelas 0/0 - 0%
- Uma estrela 0/0 - 0%
Denuncie opiniões ou materiais indevidos!
- Sugestão de aula
- Aulas
- Coleções de aulas
- Criar aula
- Criar individual
- Criar em equipe
- Gerenciar equipes
- Minhas aulas
- Orientações
- Criando equipes
- Dicas para a produção de aulas
- Reflexões pedagógicas
- Utilizando a ferramenta
- Artigo: portal educacional
- Estatísticas de uso do Portal
- Estatísticas de aulas
- Estatísticas de recursos
- Estatísticas de visitas
- Recursos utilizados em aulas
- Reflexões pedagógicas
- Informações de cursos
- Cursos
- e-Proinfo
- Materiais de cursos
- Materiais de estudo
- Artigos e publicações
- Assuntos relevantes
- Avaliações
- Ciência do cotidiano
- Destaques internacionais
- Dicas práticas
- Educação profissional e tecnológica
- Entrevistas
- Estratégias pedagógicas
- Inovações tecnológicas
- Materiais de cursos
- Materiais de evento
- Orientações e diretrizes
- Parâmetros e referencias
- Programas em vídeos
- Tutoriais
- TVescola
- Ferramentas do portal
- Fórum
- Portal do Youtube
- Compartilhando apresentação
- Ferramentas pela internet
- Blog
- Compartilhe vídeos
- Comunicação on-line
- Crie e compartilhe apresentações
- Edite e compartilhe fotos
- Escrita colaborativa
- Junte-se a uma comunicade
- Lista de discussão
- Organize e compartilhe favoritos
- Podcast
- Rádio/TVs Universitárias e outros
- Redes Sociais
- Robô Ed
PLATAFORMA FREIRE
- Bibliotecas
- Capacitação Proinfo Integrado
- Cultura
- Dicionários, tradutores e enciclopédias
- Educação inclusiva
- Geoprocessamentos
- Inclusão digital
- Infográficos
- Jogos educativos
- Jornais
- Museus
- Observatórios e planetários
- Organizações governamentais
- Plataformas educacionais
- Portais educacionais e outros
- Portal MEC
- Prêmio professores do Brasil
- Produções de professores
- Projetos de escolas
- Projetos inovadores
- Projetos sociais e educacionais
- Rádio escola
- Recursos digitais
- Revistas
- Sites de busca
- Sites temáticos do portal e TVescola
- Softwares de edição e outros
- Softwares educacionais
- Um computador por aluno

- Ryan Oksenhorn
- Ryan Snow
- Sergio Caldara
- Shane Miler
- Shane Herzog
- Sotirios Papavasilopoulos
- Stephen JB Thomas
- Tarah
- Valera Nazarov
- ZbigniewMa K Flakus

